Checking your teeth for tooth decay is just one part of a thorough dental examination. During your checkup appointment, your dentist (or dental hygienist) will likely evaluate the health of your gums, perform a head and neck examination (to look for anything out of the ordinary) and examine your mouth for any indications of oral cancer, diabetes or vitamin deficiencies. Don’t be surprised if your dentist also examines your face, bite, saliva and movement of your lower jaw joints (TMJs). Your dentist or dental hygienist will then clean your teeth and stress the importance of you maintaining good oral hygiene at home between visitsile evaluation

1. Regular oral checkups
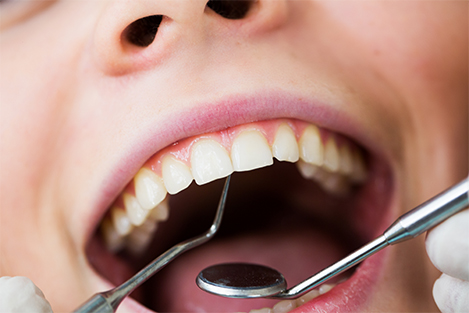
2. Teeth cleanup
Teeth cleaning (also known as prophylaxis, literally a preventive treatment of a disease) is a procedure for the removal of tartar (mineralized plaque) that may develop even with careful brushing and flossing, especially in areas that are difficult to reach in routine tooth brushing. It is often done by a dental hygienist. Professional cleaning includes tooth scaling and tooth polishing and debridement if too much tartar has accumulated. This involves the use of various instruments or devices to loosen and remove deposits from the teeth.
3. Filling And Restorations
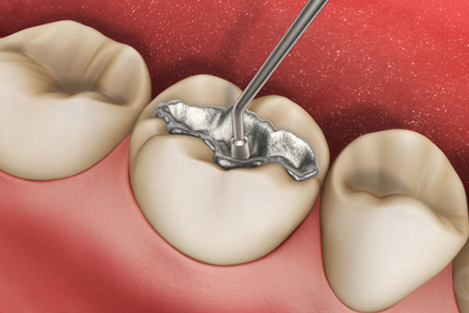
A dental restoration or dental filling is a dental restorative material used to restore the function, integrity and morphology of missing tooth structure. The structural loss typically results from caries or external trauma. It is also lost intentionally during tooth preparation to improve the aesthetics or the physical integrity of the intended restorative material. Dental restoration also refers to the replacement of missing tooth structure that is supported by dental implants.
4. RCT(Root Canal Treatment)
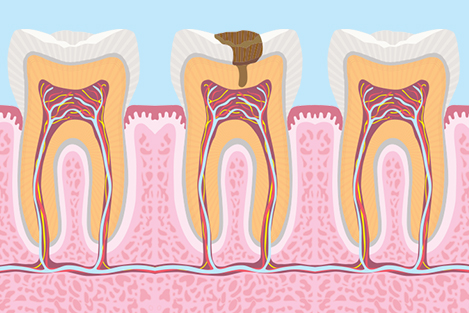
A root canal is a treatment to repair and save a badly damaged or infected tooth. The procedure involves removing the damaged area of the tooth (the pulp), cleaning and disinfecting it and then filling and sealing it. The common causes affecting the pulp are a cracked tooth, a deep cavity, repeated dental treatment to the tooth or trauma. The term "root canal" comes from cleaning of the canals inside the tooth's root.
Endodontic therapy or root canal therapy is a sequence of treatment for the infected pulp of a tooth which results in the elimination of infection and the protection of the decontaminated tooth from future microbial invasion. Root canals, and their associated pulp chamber, are the physical hollows within a tooth that are naturally inhabited by nerve tissue, blood vessels and other cellularentities. Together, these items constitute the dental pulp.Endodontic therapy involves the removal of these structures, the subsequent shaping, cleaning, and decontamination of the hollows with small files and irrigating solutions, and the obturation (filling) of the decontaminated canals. Filling of the cleaned and decontaminated canals is done with an inert filling such as gutta-percha and typically a eugenol-based cement.Epoxy resin is employed to bind gutta-percha in some root canal procedures.Endodontics includes both primary and secondary endodontic treatments as well as periradicular surgery which is generally used for teeth that still have potential for salvage.
5. Fixed teeth (crown and bridges)
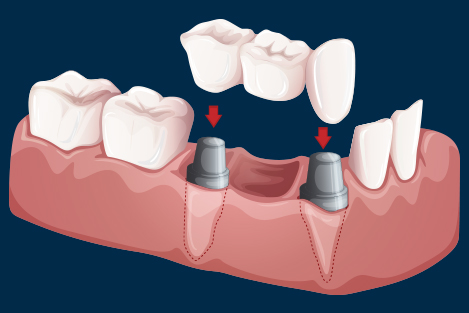
A bridge is a fixed dental restoration (a fixed dental prosthesis) used to replace a missing tooth (or several teeth) by joining an artificial tooth permanently to adjacent teeth or dental implants.
A crown is a type of dental restoration which completely caps or encircles a tooth or dental implant. Crowns are often needed when a large cavity threatens the ongoing health of a tooth.They are typically bonded to the tooth using a dental cement. Crowns can be made from many materials, which are usually fabricated using indirect methods. Crowns are often used to improve the strength or appearance of teeth. While inarguably beneficial to dental health, the procedure and materials can be relatively expensive.
6. Removable teeth
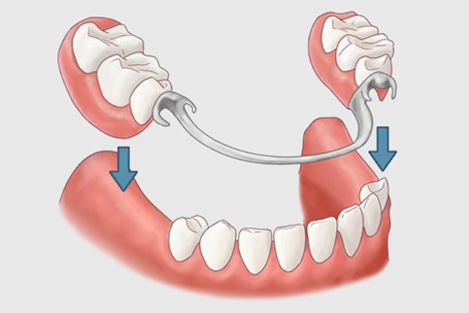
A removable partial denture (RPD) is a denture for a partially edentulous patient who desires to have replacement teeth for functional or aesthetic reasons and who cannot have a bridge (a fixed partial denture) for any number of reasons, such as a lack of required teeth to serve as support for a bridge (i.e. distal abutments) or financial limitations. This type of prosthesis is referred to as a removable partial denture because patients can remove and reinsert it when required without professional help. Conversely, a "fixed" prosthesis can and should be removed only by a dental professional.
7. Complete dentures
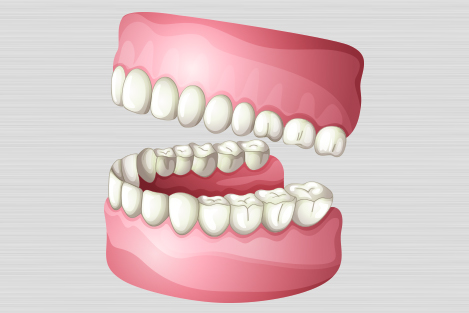
Dentures, also known as false teeth, are prosthetic devices constructed to replace missing teeth; they are supported by the surrounding soft and hard tissues of the oral cavity. Conventional dentures are removable (removable partial denture or complete denture). However, there are many denture designs, some which rely on bonding or clasping onto teeth or dental implants (fixed prosthodontics). There are two main categories of dentures, the distinction being whether they are used to replace missing teeth on the mandibular arch or on the maxillary arch.
8. Dental implants
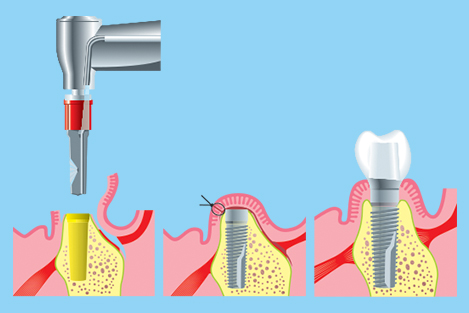
The primary use of dental implants are to support dental prosthetics. Modern dental implants make use of osseointegration, the biologic process where bone fuses tightly to the surface of specific materials such as titanium and some ceramics. The integration of implant and bone can support physical loads for decades without failure.
9. Pediatric dental care
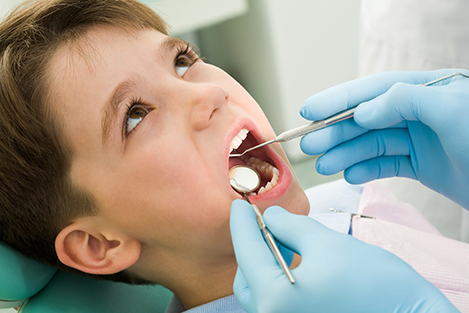
Pediatric dentistry is the specialty of dentistry that focuses on the oral health of young people. We are concerned about your child’s total health care. Good oral health is an important part of total health. Establishing us as your child’s Dental Home provides us the opportunity to implement preventive dental health habits that keep a child free from dental/oral disease. We focus on prevention, early detection and treatment of dental diseases, and keep current on the latest advances in dentistry for children. Pleasant visits to the dental office promote the establishment of trust and confidence in your child that will last a lifetime. Our goal, along with our staff, is to help all children feel good about visiting the dentist and teach them how to care for their teeth. From our special office designs to our communication style, our main concern is what is best for your child.
10. Extractions
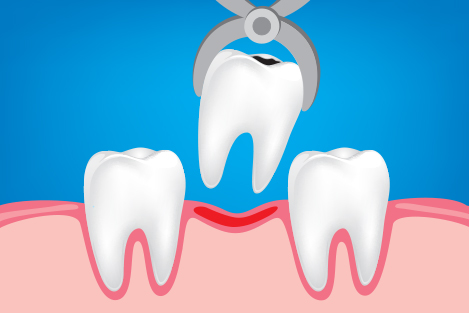
A dental extraction (also referred to as tooth extraction, exodontia, exodontics, or informally, tooth pulling) is the removal of teeth from the dental alveolus (socket) in the alveolar bone. Extractions are performed for a wide variety of reasons, but most commonly to remove teeth which have become unrestorable through tooth decay, periodontal disease or dental trauma, especially when they are associated with toothache. Sometimes wisdom teeth are impacted (stuck and unable to grow normally into the mouth) and may cause recurrent infections of the gum (pericoronitis). In orthodontics if the teeth are crowded, sound teeth may be extracted (often bicuspids) to create space so the rest of the teeth can be straightened.
11. Orthodontic treatment/braces
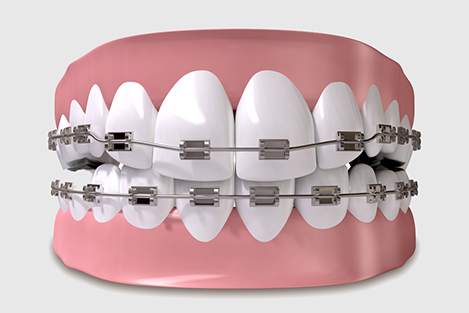
Dental braces (also known as braces, orthodontic cases, or cases) are devices used in orthodontics that align and straighten teeth and help to position them with regard to a person's bite, while also working to improve dental health. They are often used to correct underbites, as well as malocclusions, overbites, open bites, deep bites, cross bites, crooked teeth, and various other flaws of the teeth and jaw. Braces can be either cosmetic or structural. Dental braces are often used in conjunction with other orthodontic appliances to help widen the palate or jaws and to otherwise assist in shaping the teeth and jaws.
12. Superspecialized consultations
Endodontist, Periodontist, Orthodontist, Prosthodontist, Pedodontist, Oral and maxillofacial surgeon